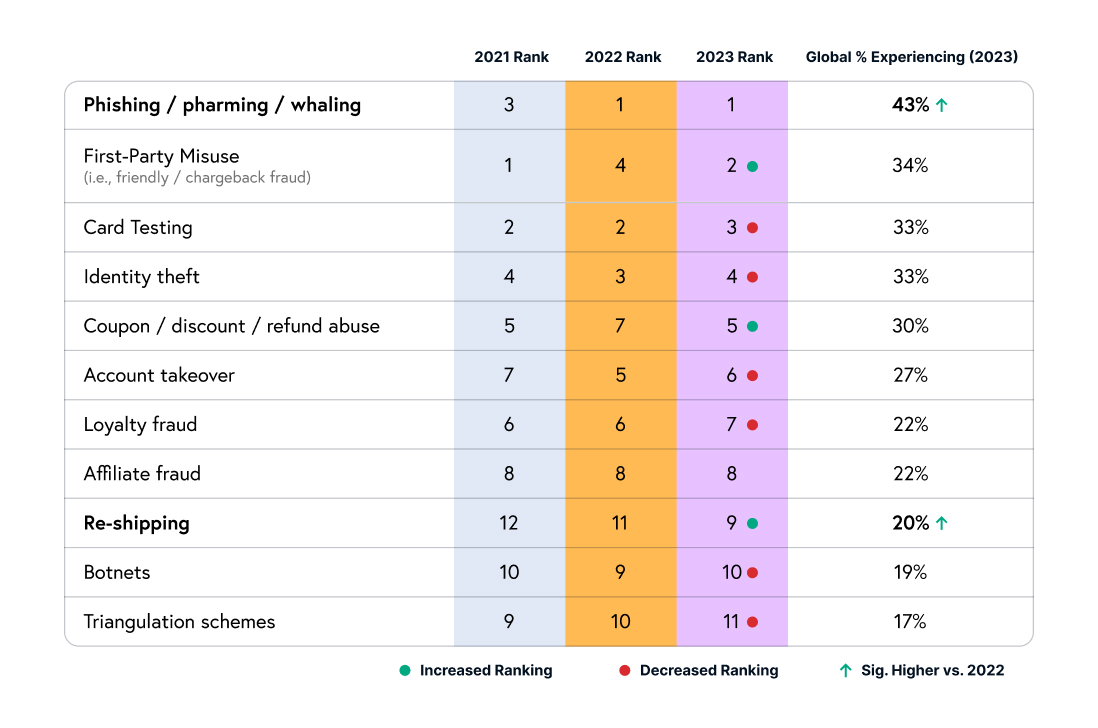
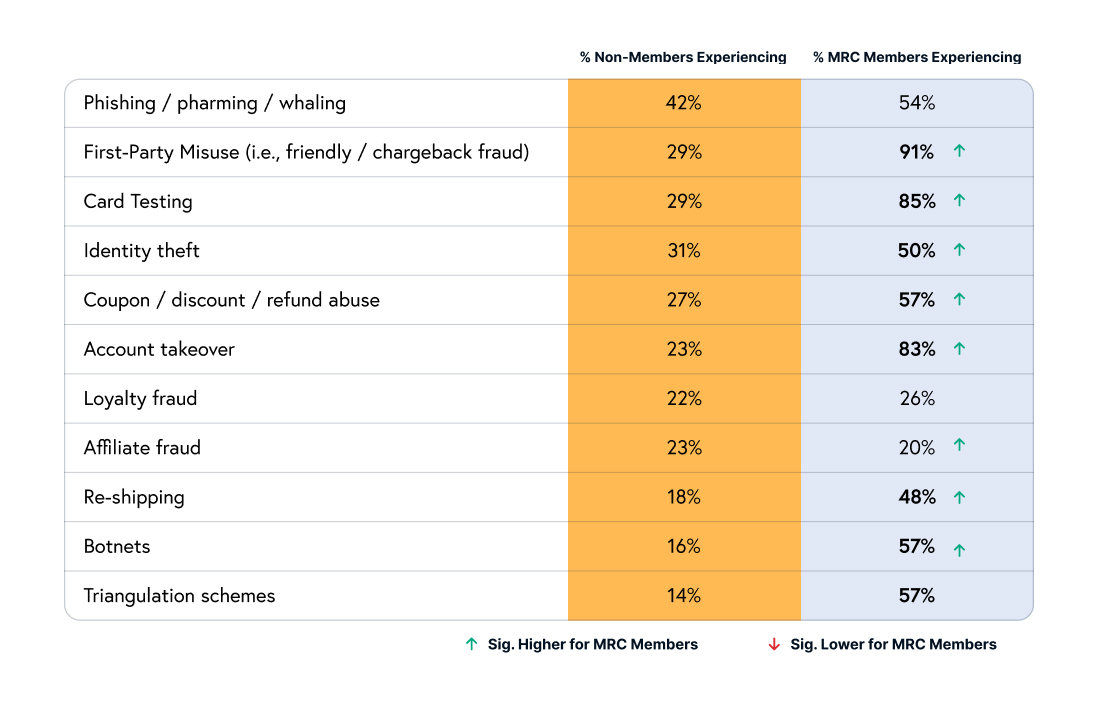
Unauthorized purchases are the underlying threat to eCommerce when it comes to the alarming trends we’re seeing across identity theft, card testing, and account takeover (ATO) attacks. These varying angles of stolen identities are creating a complex web of threats for businesses and consumers alike. Over the last five years, there has been a 68% increase in identity theft cases. Parallel to this, there has also been a spike in card testing, with as many as 85% of merchants saying they’ve experienced this type of fraud. Card testing causes direct financial losses and also serves as a gateway to broader payment fraud, allowing criminals to authenticate stolen credit card information for larger, more damaging purchases.
Fraudulent purchases make up 34% of all chargebacks. The cumulative effect of identity theft, card testing, and ATO attacks on chargebacks exacerbates operational challenges, elevating dispute resolution costs and potentially increasing penalty fees from credit card companies, making it a multifaceted problem that affects the entire payment ecosystem.
What is Identity Theft?
Identity theft involves the unauthorized acquisition and use of someone’s personal information — such as their name, social security number, or credit card details — to commit fraud or theft. In the context of eCommerce, this can lead to unauthorized transactions, account takeovers, and the opening of fraudulent accounts, causing significant financial and reputational damage to both consumers and businesses.
What is Card Testing?
Card testing, also known as carding, is a subset of identity theft in which criminals test stolen credit card numbers to verify their validity and credit limit. Fraudsters will use small transactions on websites, online services, or donation platforms that have automated payment processing systems to confirm if the stolen card details can be used for larger fraudulent purchases.
What is Account Takeover?
Account Takeover occurs when an unauthorized party gains access to a shopper’s eCommerce account, enabling them to make unauthorized purchases, siphon funds, or pilfer sensitive personal data. This fraud not only results in financial losses but can also severely damage customer trust and brand reputation.
How Stolen Identities & Unauthorized Purchases Happen
Phishing attacks
Cybercriminals acquire credit card details or account passwords through phishing, data breaches, or purchasing them on the dark web. Fraudsters may deceive shoppers — using manipulative social engineering tactics — into revealing their login credentials through fake emails or websites masquerading as legitimate businesses. Merchants can also become victims of social engineering as fraudsters trick eCommerce teams into granting access to a customer’s account.
Data breaches
Cybercriminals hack into databases of eCommerce sites to steal the personal and financial information of customers.
“>Cybercriminals hack into databases of eCommerce sites to steal the personal and financial information of customers.
Validation and exploitation
Once a card or account is verified as active, it’s used for larger fraudulent purchases or sold to other criminals.
Chargebacks and losses
Merchants face chargebacks from legitimate cardholders, incurring fees, losing out on merchandise, and consequences from exceeding chargeback thresholds.
How to Prevent Unauthorized Purchases
Monitor transactions and perform velocity checks
Implement systems to detect unusual transaction patterns, such as multiple attempts with different cards from the same IP address or logins from new devices or locations, which could indicate an ATO attempt. Use advanced fraud detection solutions that use real-time machine learning to identify and block suspicious activities.
Integrate CAPTCHA verification on payment gateways
The CAPTCHA mechanism can deter automated bots from testing card details on your site.
Employ multiple lines of authentication
Card verification value (CVV) and address verification services (AVS) can help verify that the customer possesses the physical card. Consider using MFA or 2FA for all transactions or those that are flagged as high-risk to ensure the cardholder is authorizing the purchases.
Data encryption
Utilize robust encryption standards for storing and transmitting customer data to protect it from unauthorized access.
Keep up with the latest compliance standards
Adhere to data protection regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS to ensure the highest standards of data security and privacy.
Monitor for exposed information
Use services that monitor the dark web for leaked or stolen data, allowing for prompt action if customer information is compromised.
Impart account security best practices on customers
Educate customers about the risks of phishing and the importance of secure password practices, including not reusing passwords across sites. Encourage shoppers to install reputable antivirus and anti-malware solutions on their devices to prevent keylogging and spyware.
Stay apprised of where you stand in relation to chargeback thresholds
Chargeback thresholds are predefined limits set by payment processors or acquiring banks that determine when a merchant may face consequences due to excessive chargebacks. These thresholds are in place to monitor and manage the level of chargebacks a merchant experiences, as high chargeback rates can have negative consequences for both the merchant and the payment processor.
Create effective password policies to protect accounts
Encourage or enforce strong, unique passwords through regular prompts and by blocking common or previously breached passwords. Implement stringent verification processes for any account change requests, especially those made via customer service channels.
Perform frequent security audits
Conduct periodic reviews of account security measures, and update them in response to new or evolving threats.
“It’s always interesting to see the different ways fraudsters will try to manipulate information to make orders appear legitimate. Merchants should be wary of shoppers who make repeated calls attempting to confirm an order’s legitimacy. Their demeanor can be convincing over the phone, but fraudsters are adept at social engineering, often saying exactly what is needed to win over the trust of customer service representatives, masking the illegitimacy of their orders.”
Irina Vayner,
Sr. Fraud Analyst at NoFraud
Related Threats
Payments fraud
Card testing falls into the realm of payments fraud, which includes any fraudulent or unauthorized activity that occurs during a payment transaction, typically involving the use of stolen payment information or deceptive practices to gain financial benefit illegally.
Credit grooming or bust-out fraud
A scheme where fraudsters build good credit over time using stolen or synthetic identities only to max out their credit limits without any plans of repayment.
Synthetic identities
Combining real and fake information to create new identities used to open fraudulent accounts or make purchases.